Virtualization has been one of the critical advances in this evolution, which has modernized IT infrastructure and operations. The introduction of virtualization technology allows multiple logical or virtual environments to run on a common shared infrastructure. VMware, a pioneer in virtualization, has played a crucial role in making this technology popular and dominant.
Calsoft is a VMware Technology Alliance Partner (TAP) – Elite level and has rich experience in driving the VMware ecosystem with exposure to nearly all VMware products. This makes us a one-stop consultant for the application of VMware technologies in virtualization for business.
Calsoft was proudly the primary contributor, along with VMware, in the ideation, design, and development of the NSX Migration tool. Calsoft named Maintainer of VMware (by Broadcom) NSX Migration Tool for VMware Cloud Director.
Read the blog to learn how to modernize your network infrastructure migrating to VMware NSX V to NSX T. Ultimate Guide for NSX V to NSX T Migration. However, it requires a comprehensive understanding of the difference between the two tech platforms before enterprises embark on the migration journey. Explore NSX-V and NXS-T, and the key differentiating factors between the two. Get more insights from this article Key Differences Between NSX-V and NSX-T You Need to Know Before Migration
However, following Broadcom’s $61 billion acquisition of VMware, major shifts in licensing and product models have prompted many organizations to rethink their dependence on VMware.
As organizations evolve towards more agile, scalable, and cost-efficient IT infrastructures, VMware migration has taken center stage. Enterprises are increasingly exploring VMware exit strategies in favour of next-gen platforms and cloud-native solutions. Whether it’s to migrate VMware to Azure, consider a VMware to AWS migration, or adopt a VMware alternative, this step-by-step guide helps IT leaders navigate the complexities of virtualization modernization in 2025.
As there exist many VMware alternatives, several organizations are raising the question: How to migrate from VMware to an alternative platform? What are the best practices, and the key steps involved in the migration process?
Calsoft brings together strong infrastructure expertise, agile platform capabilities, and AI-powered insights to help enterprises turn VMware migration into a business edge.
This blog provides a complete overview of the following:
What is VMware Migration and Why to Migrate?
VMware migration is the process of transitioning virtual machines, applications, data, and associated workloads from VMware infrastructure to alternate platforms such as Nutanix, Red Hat OpenShift, Proxmox, OpenStack, or public cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
The change in VMware Licensing causes several main challenges to the clients. VMware will shift to a term-based, subscription-based, and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) license. Additionally, Broadcom removed the ability to extend the maintenance Software and Services (SnS) on existing perpetual licenses.
Other key factors that can motivate a migration from VMware are listed below in the image:
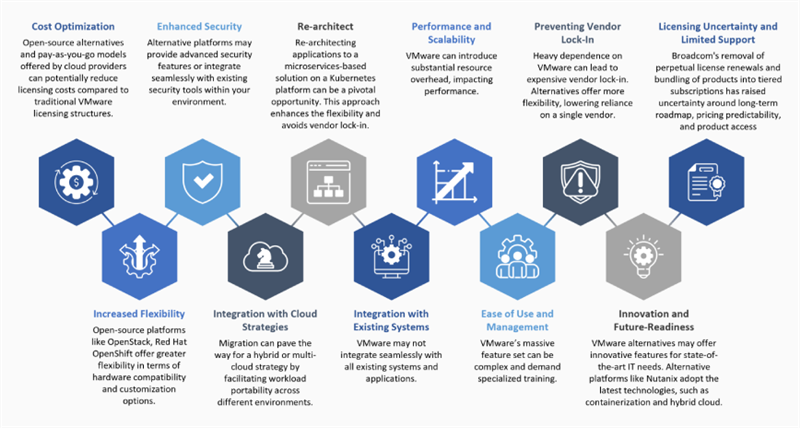
Let us now explore the key challenges imposed on customer businesses.
Download our latest whitepaper to get more insights.
Challenges Imposed and the Impact on Customer Business
The VMware acquisition has financial and operational consequences for current customers, who are forced to adapt to maintain their operations.

How to Overcome the Challenges
There are three main migration options available to tackle these challenges and minimize the impact to the business:
- Retain on-premises Compute: keep the level of change and disruption to the as-is situation as low as possible
- Reduce Impact and gain time to act utilize VMware on cloud to quickly move workloads and mitigate OPEX impact, avail fix license costs for a short term and retire on- premises VMware products.
- Accelerate to Public Cloud: Accelerate the cloud journey and benefit from native solutions. An investment to benefit in the long term.
The other proactive steps to mitigate the risks and navigate the post-acquisition landscape are:
- Build Expertise: Invest in training and upskilling your IT staff to manage potential migrations, troubleshoot technical issues, and adapt to changes in the VMware ecosystem.
- Stay Informed: Closely monitor Broadcom’s announcements, roadmap updates, and customer communications to anticipate changes and plan accordingly.
- Seek Partnerships: Collaborate with other SMEs, industry associations, and technology partners to share knowledge, insights, and best practices for navigating the post-acquisition landscape.
A successful migration depends on careful planning and thorough preparation. The migration process involves essential steps to evaluate your current environment, identify potential challenges, and develop a comprehensive migration strategy. By diligently following proper strategies, you can mitigate risks, optimize resource allocation, and ensure a smooth transition to the new platform.
A well-defined migration process is essential for a successful transition. It ensures minimal downtime, data loss prevention, and optimized resource utilization in the target environment.
Overview of Migration Workflow
The comprehensive migration workflow incorporates the following key phases in the process:
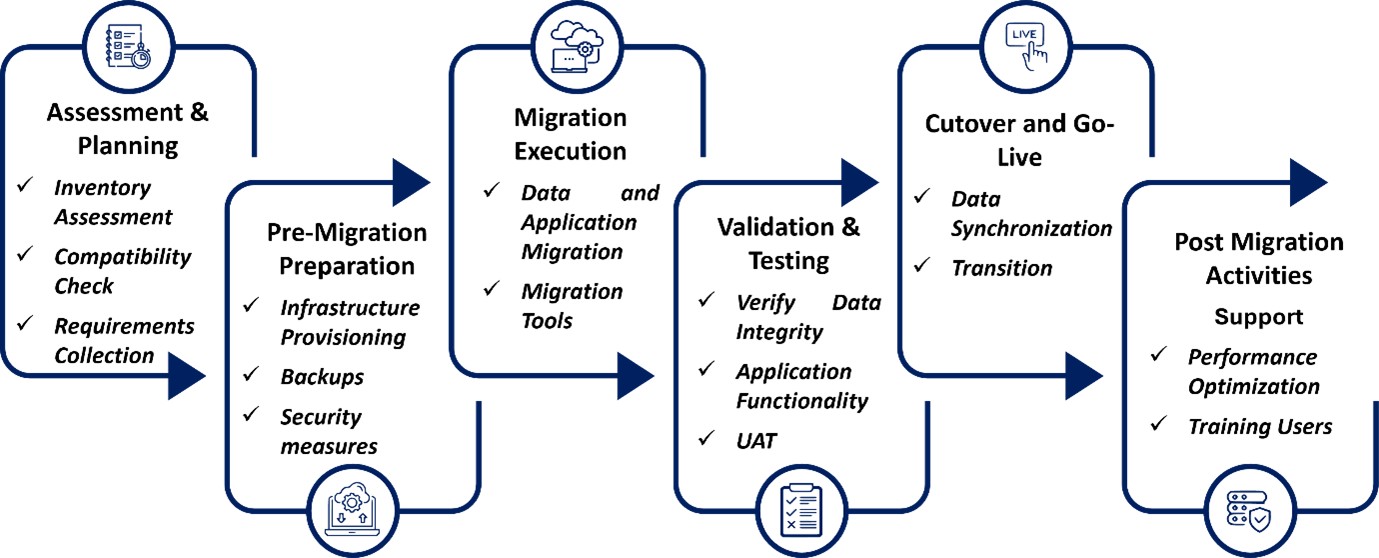
Image: VMware Migration Workflow
Assessment & Planning: The migration process begins with a comprehensive assessment and strategic planning phase. This includes:
- Defining migration goals, scope, and constraints
- Evaluating the existing VMware environment (hardware, software, and workloads)
- Performing risk assessments and estimating costs
- Designing the target architecture and migration strategy
Pre-Migration Preparations: This stage focuses on preparing the destination platform:
- Provisioning the necessary infrastructure
- Performing full backups of critical data and configurations
- Implementing security policies and access controls
- Conducting initial compatibility checks and dry runs
- Preparation helps mitigate risks and ensures that the target platform is ready to receive workloads.
Migration Execution: This phase involves the actual migration of workloads, applications, and configurations using specialized tools and automated scripts. Depending on the chosen platform, tools like: virt-v2v, CloudEndure, or platform-native utilities (e.g., Nutanix Move, Red Hat MTV) are used to perform live or staged migrations. Attention should be given to minimizing downtime and handling interdependent workloads in batches.
Validation and Testing: This stage is critical to confirm that the migration was successful and that the system performs as required.
After migration:
- Validate data integrity
- Test application functionality
- Verify network, storage, and security configurations
- Conduct User Acceptance Testing (UAT) to ensure the new environment meets operational and user expectations
Cutover and Go-Live: The cutover phase involve:
- Final synchronization of any delta changes
- Switching production traffic to the new platform
- Closely monitoring system behaviour during the initial post-migration period
- A rollback or contingency plan should be in place in case issues arise during go-live.
Post-Migration Activities: Post-migration tasks include:
- Providing technical support to users
- Optimizing performance and tuning the infrastructure
- Updating operational and architectural documentation
- Training end-users and administrators
- Configuring additional services (e.g., backup, DR, monitoring)
- Comprehensive testing is repeated to ensure all systems are stable and aligned with SLAs.
Continuous Improvement
Request feedback from users and IT staff to identify areas for improvement and address any ongoing challenges or issues.
Stay Updated
Stay updated on advancements in the chosen alternative platform to utilise innovative features and capabilities for constant optimization.
A well-structured migration workflow from VMware to an alternative platform ensures that organizations can leverage the benefits of their new infrastructure, achieving greater efficiency and innovation.
Organizations looking for VMware alternatives can look at a range of options such as open-source hypervisors like KVM and Xen, commercial platforms such as Red Hat Virtualization, and hyper-converged solutions like Nutanix Cloud Infrastructure.
How Calsoft Supports Your Migration Agenda
Calsoft is a technology-first and trusted partner for Migration Services, offering comprehensive solutions to help businesses move their data and resources safely and efficiently.
Calsoft understands the technical challenges of migrating from VMware. We provide a comprehensive solution that addresses key issues such as data migration, system compatibility, minimizing data loss, and optimizing resource allocation. Our approach simplifies the migration process, reduces risks, and ensures a seamless transition with improved operational efficiency.
We approach migration not as a standalone project but as a platform evolution strategy.
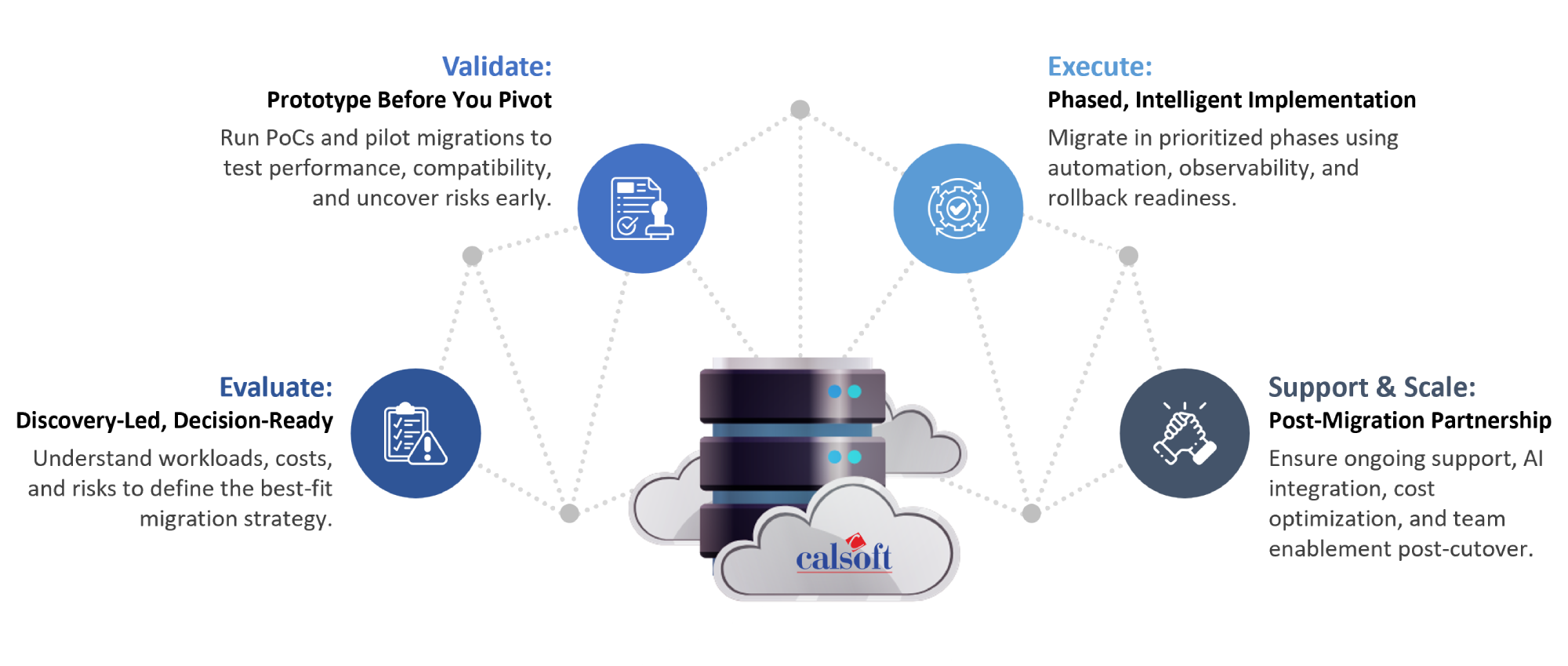
Calsoft combine deep infrastructure expertise, agile platform skills, and AI-driven intelligence to turn VMware migration into a competitive advantage. Our holistic methodology ensures a smooth transition while laying the groundwork for a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective future.
Let us now delve into the top VMware alternatives and their key features.
Top VMware Alternatives & Competitors for Virtual Workload Solutions
Here, we will explore the leading VMware alternatives, providing insights from industry experts and highlighting each platform’s characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages as detailed in the table below.
| Platform | Cost | Scalability | Pros | Cons | Ideal Use Case | Community/Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenShift | High (subscription model) | Highly scalable with Kubernetes integration | Strong security, enterprise-ready features | Steep learning curve, vendor lock-in | Enterprises needing robust CI/CD and security | Strong Red Hat support |
| Azure | Pay-as-you-go; can be expensive at scale | Excellent, globally distributed | Seamless integration with Microsoft stack | May be costly for small projects | Hybrid cloud deployments | Microsoft-backed support |
| AWS | Pay-as-you-go; cost-effective at scale | Highly scalable with large feature set | Widest range of services | Complex billing, learning curve | Scalable cloud-native apps | Large community + AWS support |
| OpenStack | Lower overall; open source | Scalable but requires manual setup | Open & customizable | Steep learning curve | Private clouds, research orgs | Active open-source community |
| KVM | Free (open source) | Scalable to adequate setups | Lightweight, affordable, stable | Less user-friendly, lower performance than others | Lightweight virtual machines | Linux community |
| VMware | High licensing and support costs | Highly scalable with vSphere suite | Robust virtualization features | Licensing costs, less flexible | Enterprise data centers | Extensive documentation |
Reference: Top VMWare Alternatives
In Summary
The Broadcom acquisition of VMware introduces significant uncertainty for many enterprises—ranging from increased licensing costs to strategic shifts that could limit innovation and flexibility. However, with proactive planning and informed decision-making, organizations can turn this disruption into a catalyst for modernization.
Migrating from VMware is not just a defensive move—it’s an opportunity to enhance agility, improve cost efficiency, and strengthen security posture. By adopting a structured migration approach, using the right automation and tooling, and prioritizing security and compliance, enterprises can ensure a smooth, future-ready transition to a platform that aligns with their evolving needs.






