To understand what a datacenter is, first let us recall what a computer is. A computer consists of three major components—CPU (computation), Memory (RAM) and Disk (storage). Similarly, a datacenter used to have three discrete and interconnected components—Servers (for compute), Storage Array (for storage), and Network Switches (for connectivity). These components evolved in time and thus contributed to the evolution of datacenters.
Datacenter Components
Server
The most important part of a server/computer is its processor. The evolution of CPU/processors happened over its number of COREs (logical processor) to represent a physical processor. From single core, dual core, to multi core—that is the journey of processors.
Storage
Storage evolved from a 1.4 MB Floppy (as I know), 700 MB CD to 2 TB USB, and 30 TB SSDs. The protocols to connect to these storages started from IDE, SCSI, SAS to SATA, PATA to today’s NVMe.
Networking
Networking evolved from 10 MBPS to today’s 100 GBPS. The devices changed from hubs, switches to routers, firewalls, and so on. The topologies evolved from LAN to WiFi and WAN.
Virtualization
All these discrete components were playing their vital roles and then came the era of virtualization. In virtualization, the physical components were divided into logical ones and then represented to an application as multiple physical components.
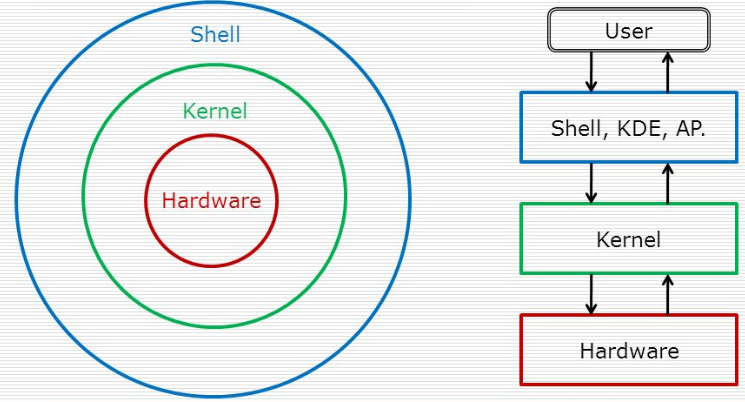
All the building blocks (hardware, kernel, user space) of a computer were virtualized as hardware virtualization, memory virtualization, software virtualization, network virtualization, application virtualization, storage virtualization, and so on. With virtualization, things that were seemingly impossible earlier became possible.
A single computer can play multiple operating systems. All operating systems boot at the same time as a virtual machine. All virtual machines run as an application on a single kernel called hypervisor. A set of virtual machines forms a cluster to serve a single service or application. A single storage disk shared across multiple servers forms a storage cluster.
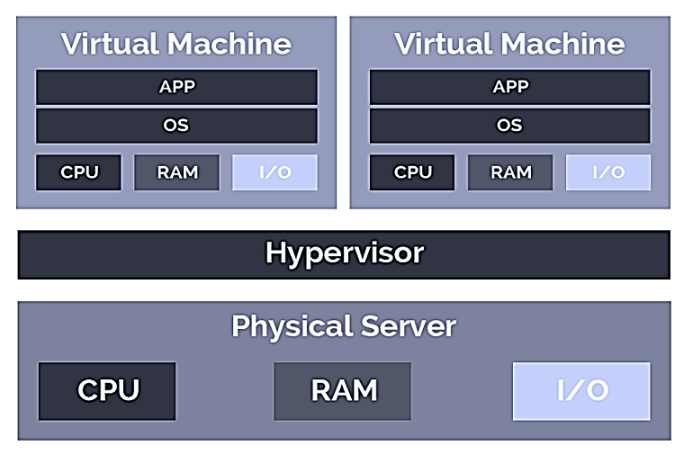
Converged Infrastructure:
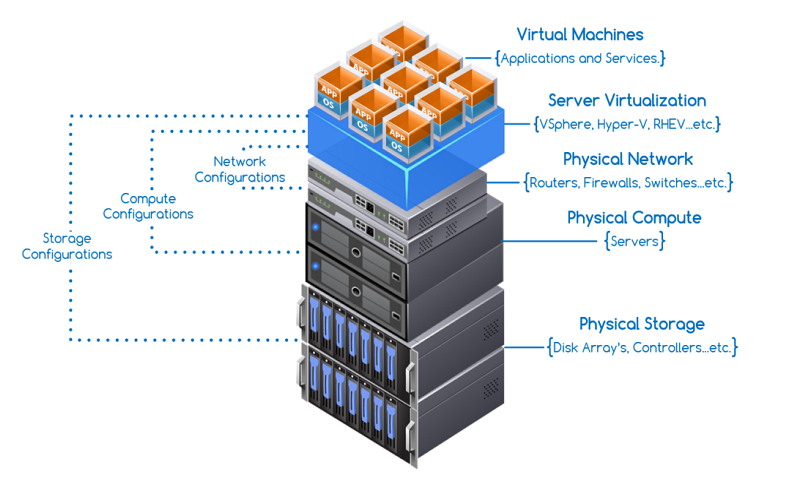
The idea of component virtualization, their integration, and management gave rise to a term called Converged Infrastructure OR CI. In CI, the various components are grouped together to form a single CI-Node. Datacenter administrators get a single management utility/interface to manage all the components of CI. This discrete component management via a single interface allowed CI to serve features such as scale out, scale up, high availability, and so on.
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure:
Then came the era of software-defined components. Software-defined network, software-defined storage, software-defined compute, which then formed software-defined infrastructure. The term “software-defined†implies that the services expected out of physical devices were getting programmed and performed through a piece(s) of code running on a single node. This reduced the need of discrete components and gave rise to a term called Hyper Converged Infrastructure or HCI.
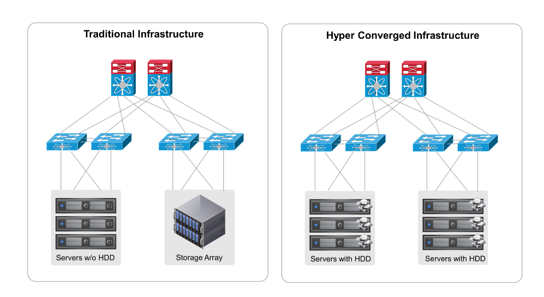
In HCI, all the programs of discrete components are clubbed together to form a single HCI-Node. As the components are software-defined and integrated together in a node, managing them through an external interface is easy. What is difficult is achieving feasibility of scale out and scale up.
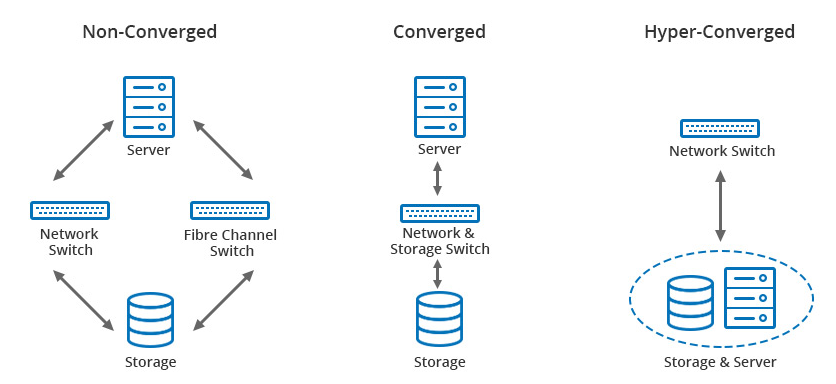
In a nutshell, the clubbing of individual components of a datacenter to form a single node is called converged infrastructure. Clubbing of software-defined components to form a node is called HCI.
The next era will be of hybrid infrastructure which will be a mash-up of hardware-based and software-based components.






